Java - 캡슐을 나누기
앞 게시글에서는 캡슐화를 완성했다.
여기서 캡슐을 더나눌수 있지않을까 ?
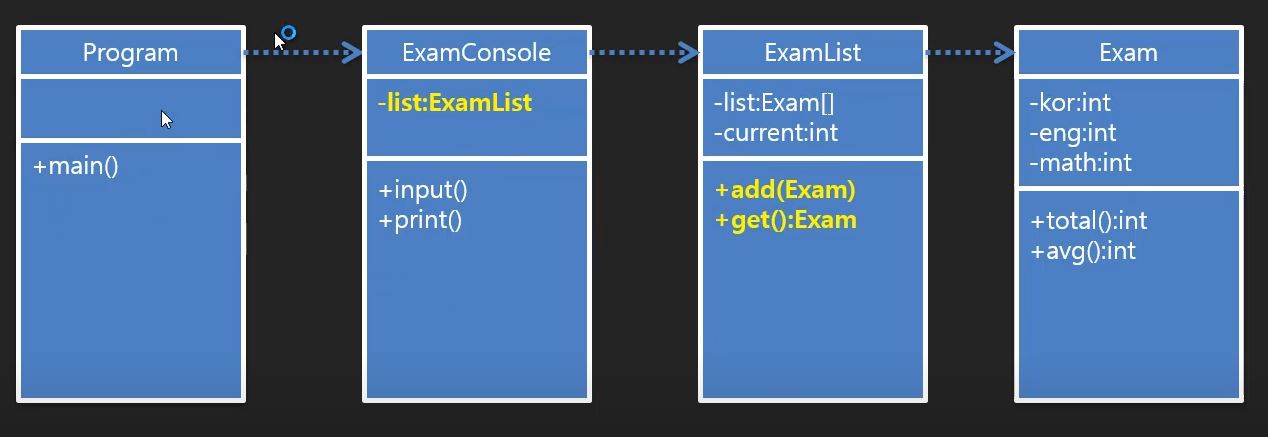
Program main()
↓
ExamConsole -list:ExamList +input() +print()
↓
ExamList -list:Exam[] -current:int +add(Exam) +get():Exam
↓
Exam -kor:int -eng:int -math:int +total()/int +avg():int
이런구조가 되게 분리할것이다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExamList {
private Exam[] exams;
private int current;
public void printList() {
this.printList(this.current);
}
public void printList(int size) {
System.out.println("┌──────────────────┐");
System.out.println("│ 성적 출력 │");
System.out.println("└──────────────────┘");
System.out.println();
//int size = list.current;
for(int i= 0; i<size; i++ ) {
Exam exam = this.get(i);//
int kor = exam.getKor(); //exam.kor;
int eng = exam.getEng();
int math = exam.getMath();
int total = exam.total(); //kor+eng+math;
float avg= exam.avg();// total/3.0f;
System.out.printf("국어 :%d\n", kor);
System.out.printf("영어 :%d\n", eng);
System.out.printf("수학 :%d\n", math);
System.out.printf("총점 : %3d\n", total);
System.out.printf("평균 : %6.2f\n", avg);
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
}
private Exam get(int i) {
return this.exams[i];
}
public void inputList() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("┌──────────────────┐");
System.out.println("│ 성적 입력 │");
System.out.println("└──────────────────┘");
System.out.println();
int kor, eng, math;
do {
System.out.printf("국어 :");
kor = scan.nextInt();
if(kor < 0 || 100 < kor)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(kor<0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어 :");
eng = scan.nextInt();
if(eng < 0 || 100 < eng)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(eng<0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학 :");
math = scan.nextInt();
if(math < 0 || 100 < math)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(math<0 || 100 < math);
/*
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.setKor(kor); //exam.kor=kor;
exam.setEng(eng);
exam.setMath(math);
*/
Exam exam = new Exam(kor,eng,math);
// 데이터 추가-----------------------------------
add(exam);
}
private void add(Exam exam) {
Exam[] exams = this.exams;
int size = this.current;
if(exams.length == size) {
//1. 크기가 5개 정도 더큰 새 배열을 생성하시오
Exam [] temp = new Exam[exams.length +5];
//2. 값을 이주시키기
for(int i=0; i<size;i++)
temp[i] = exams[i];
//3. list.exams가 새로만든 temp 배열을 참조하도록 한다.
this.exams = temp;
}
this.exams[this.current] = exam; // 꼭해줘야하는 작업
this.current++;
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
public ExamList() {
this.exams = new Exam[3];
this.current=0;
}
}
add, get,input print 를 분리하였다.
완성
- Program
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExamConsole list = new ExamConsole();
int menu;
boolean keepLoop = true;
while(keepLoop)
{
menu =inputMenu();
switch(menu)
{
case 1:
//ExamList.inputList(list);
list.inputList();
break;
case 2:
//ExamList.printList(list);
list.printList();
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Bye~~");
keepLoop = false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 값을 입력하셨습니다. 메뉴는 1~3까지입니다.");
}
}
}
static int inputMenu() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("┌──────────────────┐");
System.out.println("│ 메인 메뉴 │");
System.out.println("└──────────────────┘");
System.out.println("\t1. 성적입력 ");
System.out.println("\t2. 성적출력 ");
System.out.println("\t3. 종료 ");
System.out.print("\t선택> ");
int menu = scan.nextInt();
return menu;
}
}
- ExamConsole ```java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExamConsole {
private ExamList list = new ExamList();
public void printList() {
this.printList(list.size());
}
public void printList(int size) {
System.out.println("┌──────────────────┐");
System.out.println("│ 성적 출력 │");
System.out.println("└──────────────────┘");
System.out.println();
//int size = list.current;
for(int i= 0; i<size; i++ ) {
Exam exam = list.get(i);//
int kor = exam.getKor(); //exam.kor;
int eng = exam.getEng();
int math = exam.getMath();
int total = exam.total(); //kor+eng+math;
float avg= exam.avg();// total/3.0f;
System.out.printf("국어 :%d\n", kor);
System.out.printf("영어 :%d\n", eng);
System.out.printf("수학 :%d\n", math);
System.out.printf("총점 : %3d\n", total);
System.out.printf("평균 : %6.2f\n", avg);
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
}
public void inputList() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("┌──────────────────┐");
System.out.println("│ 성적 입력 │");
System.out.println("└──────────────────┘");
System.out.println();
int kor, eng, math;
do {
System.out.printf("국어 :");
kor = scan.nextInt();
if(kor < 0 || 100 < kor)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(kor<0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어 :");
eng = scan.nextInt();
if(eng < 0 || 100 < eng)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(eng<0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학 :");
math = scan.nextInt();
if(math < 0 || 100 < math)
{
System.out.println("국어성적은 0~100까지의 범위만 입력이 가능합니다.");
}
}while(math<0 || 100 < math);
/*
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.setKor(kor); //exam.kor=kor;
exam.setEng(eng);
exam.setMath(math);
*/
Exam exam = new Exam(kor,eng,math);
// 데이터 추가-----------------------------------
list.add(exam);
} }
3. ExamList
```java
public class ExamList {
private Exam[] exams;
private int current;
public Exam get(int i) {
return this.exams[i];
}
public void add(Exam exam) {
Exam[] exams = this.exams;
int size = this.current;
if(exams.length == size) {
//1. 크기가 5개 정도 더큰 새 배열을 생성하시오
Exam [] temp = new Exam[exams.length +5];
//2. 값을 이주시키기
for(int i=0; i<size;i++)
temp[i] = exams[i];
//3. list.exams가 새로만든 temp 배열을 참조하도록 한다.
this.exams = temp;
}
this.exams[this.current] = exam; // 꼭해줘야하는 작업
this.current++;
System.out.println("────────────────────────");
}
public ExamList() {
this.exams = new Exam[3];
this.current=0;
}
public int size() {
return current;
}
}
- Exam ```java
public class Exam { int kor; int eng; int math;
public Exam() {
this(0, 0, 0);
}
public Exam(int kor, int eng, int math) {
this.kor= kor;
this.eng=eng;
this.math=math;
}
public int getKor() {
return kor;
}
public void setKor(int kor) {
this.kor = kor;
}
public int getEng() {
return eng;
}
public void setEng(int eng) {
this.eng = eng;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int total() {
return kor+eng+math;
}
public float avg() {
return total()/3.0f;
}
}
```
- 내가 해본 연습문제를 가지고 캡슐화를 해보자
참고 :https://youtu.be/6wKyPg9rxtw

댓글남기기