Java - 반복문
반복문
조건을 반복하는 동안 {} 를 수행 ( 0~n 번 ) -> for문과 while 문이 있다.
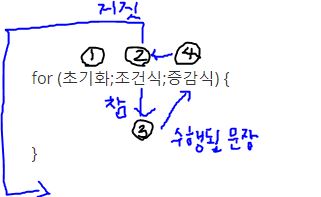
for 문
어떤 작업이 반복적으로 수행되도록 할 때 사용
나의 발그림…..
예제)1
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//반복문(for, while문 )
//1 부터 100까지의 합 구하기
int sum = 0; // for 문 안에다가 선언하면안된다. 밖에서도 쓰기위해 밖에다가 선언함
for(int i=1; i<=100; i++) { // i 가 1부터 1000보다 작거나 같은동안에 1씩증가한다.
sum = sum+i; // sum에 i를 누적해서 넣음
}
System.out.println("1~100까지의 합:" +sum);
// 1 ~ 100 짝수의 합 2+4+6+8.. +100
sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=100; i=i+2) {
sum=sum+i;
}
System.out.println("0~100까지의 짝수의 합:" +sum);
// 1 ~ 100 홀수의 합
int tot = 0;
for(int i =1; i<=100; i=i+2) {
tot=tot+i;
}
System.out.println("1~100까지의 홀수의 합:" +tot);
}
}
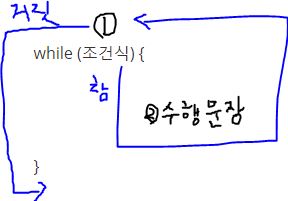
while문
조건식이 ‘참(true)인 동안’, ‘즉, 조건식이 거짓이 될 때따기 블럭 {}내의 문장을 반복’
- 조건식이 참 (ture) 이면 블럭{} 안에 들어가고, 거짓(false)이면 while 문을 벗어난다.
- 블럭{}의 문장을 수행하고 다시 조건식으로 돌아간다.
예제)2
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int tot=0;
int i= 0;
while(i<=100) {
tot = tot +i ;
i= i+1;
}
System.out.println("1~100까지의 합:" +tot);
tot=0;
i=0;
while(i<100) {
i= i+2;
tot = tot+i ;
}
System.out.println("0~100까지의 짝수의 합:" +tot);
tot=0;
i=1;
while(i<100) {
tot = tot+i;
i= i+2;
}
System.out.println("0~100까지의 홀수 의 합:" +tot);
}
}
출력값은 앞에 for문과 같다.
for문과 while문은 항상 서로 변환이 가능하다.


댓글남기기